Research Projects
Strategic Grants (NPRP)
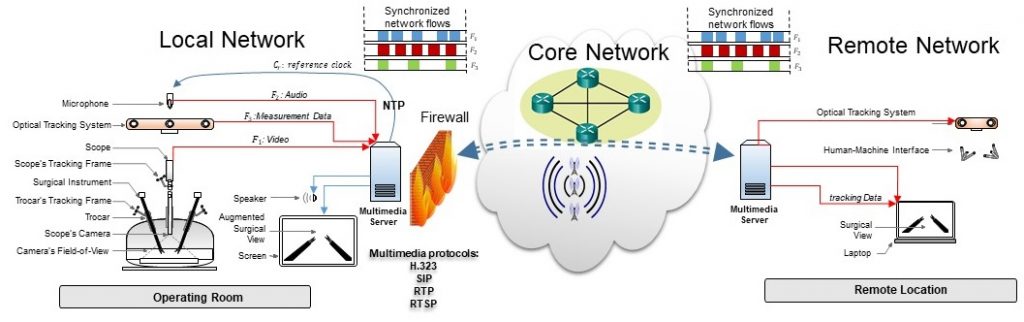 The goal of this applied research is to develop a telemedicine system to support intraoperative collaboration between a specialist/expert surgeon (who could be remotely located) and an operating surgeon during minimally invasive surgery. The project entails development of immersive, augmented reality-based, enabling technologies that would provide the operating surgeon realistic audio-visual cues from a specialist expert surgeon. The cues will assist the operating surgeon to learn and perform precise movements of the highly-actuated surgical instruments required during a minimally invasive surgery including information related to tool-tissue interaction. As the telemedicine system will provide real-time, interactive intraoperative guidance during the surgery, we hypothesize the usage of such system will facilitate efficient transfer of surgical expertise from the experienced specialist surgeon to the novice operating surgeon. This will improve the surgical outcome especially in case of specialized surgeries for treatment of cancer and renal diseases, expand the reachability, and broaden the spectrum of surgical services, thus potentially transforming the surgical care offered by hospitals. In the proposed applied research, new core technologies that will form the functional building blocks of the tele-medicine system will be pursued by a multidisciplinary team comprising of scientists/engineers (in the fields of computer graphics, human-machine interfacing, computer networking, and system integration) and clinicians (colorectal surgeons, urologists, and transplant surgeons). These core technologies, primarily comprising of human-machine interfacing, augmented reality, and computer networking, will be developed as independent modules and will be integrated together to form a unified telemedicine system during the course of the project. The integrated telemedicine system will be validated by surgeons at Hamad Medical Corporation from different specialties, including Colorectal-Surgery, Urology, and Transplant Unit. The validation studies will aim at assessing the telemedicine system as a surgical education tool as well as user-evaluation for intraoperative tele-mentoring. INTELLECTUAL MERIT: The proposed application-driven research will advance the field of telemedicine for minimally invasive surgeries by developing new enabling/core technologies. Specifically, this research will develop and advance: ▪ Human-machine interfacing technologies to capture and convert surgeon’s hand gesture into virtual surgical tool motion. ▪ Augmentation methods to enhance the surgical view by overlaying motion of virtual surgical tools. ▪ Secure networking protocols to transmit live audio-video streams over the network with packets of augmentation data. ▪ Computational frameworks to integrate the software modules with the hardware components into a single synchronized telemedicine system. The developed technological components of the integrated telemedicine system will be evaluated and clinically assessed by surgeons at Hamad Medical Corporation. This would further improve the understanding and advance the knowledge related to implementation of telemedicine technology for: ▪ Utilization across disciplines related to tele-mentoring, tele-conferencing, and tele-collaboration during a minimally invasive robotic/laparoscopic surgery. ▪ Application to minimally invasive surgical treatments (such as colectomy, radical prostatectomy, partial/radical nephrectomy, living donor nephrectomy, and pyeloplasty) of renal and cancer diseases. ▪ Assimilation into the surgical workflow across hospitals of Hamad Medical Corporation and healthcare services in Qatar. BROADER IMPACTS: The proposed research, by advancing telemedicine technology for minimally invasive surgery, can potentially have significant benefits to both patients and healthcare system in regards to surgical treatment for cancer and renal diseases. The technology will behave as a training tool for surgeons to get trained on new or improved existing MIS techniques / surgical workflows, thus improving the surgical outcome and providing higher quality of surgical care. As the technology facilitates transfer of surgical expertise, it would expand the range of specialized minimally invasive surgical services offered by a hospital to its patients. Thus, improving the capacity building for an integrated healthcare system in Qatar and delivering high impact to the patients and their families.
The goal of this applied research is to develop a telemedicine system to support intraoperative collaboration between a specialist/expert surgeon (who could be remotely located) and an operating surgeon during minimally invasive surgery. The project entails development of immersive, augmented reality-based, enabling technologies that would provide the operating surgeon realistic audio-visual cues from a specialist expert surgeon. The cues will assist the operating surgeon to learn and perform precise movements of the highly-actuated surgical instruments required during a minimally invasive surgery including information related to tool-tissue interaction. As the telemedicine system will provide real-time, interactive intraoperative guidance during the surgery, we hypothesize the usage of such system will facilitate efficient transfer of surgical expertise from the experienced specialist surgeon to the novice operating surgeon. This will improve the surgical outcome especially in case of specialized surgeries for treatment of cancer and renal diseases, expand the reachability, and broaden the spectrum of surgical services, thus potentially transforming the surgical care offered by hospitals. In the proposed applied research, new core technologies that will form the functional building blocks of the tele-medicine system will be pursued by a multidisciplinary team comprising of scientists/engineers (in the fields of computer graphics, human-machine interfacing, computer networking, and system integration) and clinicians (colorectal surgeons, urologists, and transplant surgeons). These core technologies, primarily comprising of human-machine interfacing, augmented reality, and computer networking, will be developed as independent modules and will be integrated together to form a unified telemedicine system during the course of the project. The integrated telemedicine system will be validated by surgeons at Hamad Medical Corporation from different specialties, including Colorectal-Surgery, Urology, and Transplant Unit. The validation studies will aim at assessing the telemedicine system as a surgical education tool as well as user-evaluation for intraoperative tele-mentoring. INTELLECTUAL MERIT: The proposed application-driven research will advance the field of telemedicine for minimally invasive surgeries by developing new enabling/core technologies. Specifically, this research will develop and advance: ▪ Human-machine interfacing technologies to capture and convert surgeon’s hand gesture into virtual surgical tool motion. ▪ Augmentation methods to enhance the surgical view by overlaying motion of virtual surgical tools. ▪ Secure networking protocols to transmit live audio-video streams over the network with packets of augmentation data. ▪ Computational frameworks to integrate the software modules with the hardware components into a single synchronized telemedicine system. The developed technological components of the integrated telemedicine system will be evaluated and clinically assessed by surgeons at Hamad Medical Corporation. This would further improve the understanding and advance the knowledge related to implementation of telemedicine technology for: ▪ Utilization across disciplines related to tele-mentoring, tele-conferencing, and tele-collaboration during a minimally invasive robotic/laparoscopic surgery. ▪ Application to minimally invasive surgical treatments (such as colectomy, radical prostatectomy, partial/radical nephrectomy, living donor nephrectomy, and pyeloplasty) of renal and cancer diseases. ▪ Assimilation into the surgical workflow across hospitals of Hamad Medical Corporation and healthcare services in Qatar. BROADER IMPACTS: The proposed research, by advancing telemedicine technology for minimally invasive surgery, can potentially have significant benefits to both patients and healthcare system in regards to surgical treatment for cancer and renal diseases. The technology will behave as a training tool for surgeons to get trained on new or improved existing MIS techniques / surgical workflows, thus improving the surgical outcome and providing higher quality of surgical care. As the technology facilitates transfer of surgical expertise, it would expand the range of specialized minimally invasive surgical services offered by a hospital to its patients. Thus, improving the capacity building for an integrated healthcare system in Qatar and delivering high impact to the patients and their families.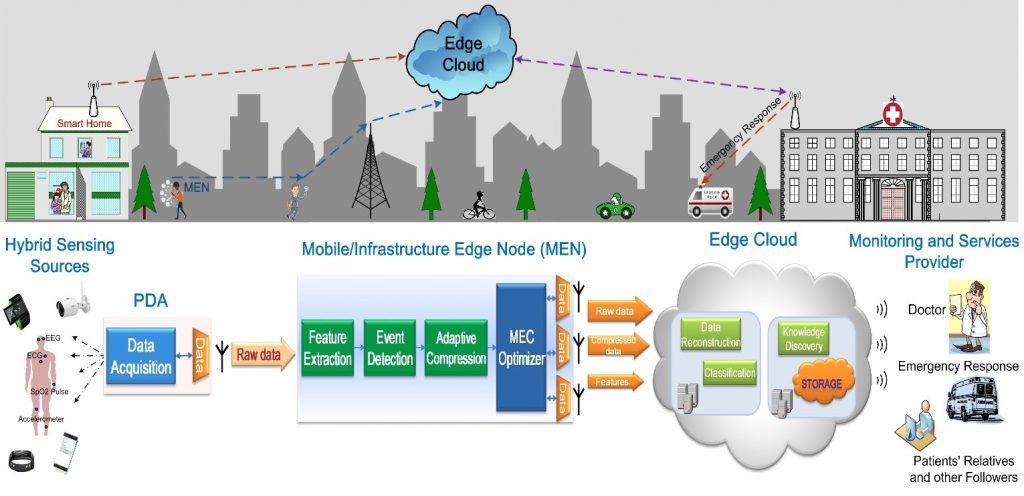 The percentage of chronic disease (CD) patients is climbing to reach almost one-fifth globally, posing immediate threats on healthcare expenditure (in Qatar it reaches ~2.5% of the national GDP), and rising causes of death (more than 76% of deaths in Qatar are owed to CDs). This calls for transforming healthcare systems away from one-on-one patient treatment, to improve services, access and scalability, while reducing costs. The deployment of mobile and wearable devices in healthcare along with the advances of wireless networking and cloud-based technologies will enable mobile health (mHealth) systems to operate in conjunction with invaluable sets of data that are amassed from wide range of sources. Smart Health (sHealth) can be considered the evolution of mHealth, where collected medical and physiological data can be efficiently mined at the patient level to better understand the patient context, hence optimizing the transmission and integration of diagnostic information from healthcare professionals at the cloud level, while facilitating immediate response in cases of emergency. Such concept is set to revolutionize healthcare delivery by giving CD patients better control of their medical situation and allow the public to continuously and smartly monitor their health conditions. Recent innovations are paving the way towards an even more interactive connectivity level with the ongoing developments towards the 5G cellular technology and the Tactile Internet, especially with the 5G massive machine type communications (mMTC) and ultra-reliable low latency communications (URLLC) use case scenarios. Combining extremely low latency with high availability and reliability, the Tactile Internet, based on 5G URLLC, will facilitate real-time, synchronous, haptic feedback with remote-control solutions. This will give rise to a great variety of opportunities for emerging technologies and services especially in the field of tele-health. With the prospective evolution towards next generation 5G networks, such services will benefit from faster connections, greater mobility, increased inter-device compatibility, and harmonization between different communications standards. Remarkably, in sHealth systems for neurological applications, continuous sensory data acquisition and rapid diagnostic feedback and medical intervention have the potential to positively impact the lives of a large portion of the global population who suffer from chronic brain illnesses and disorders. Yet, these impose strict constraints on data storage, capabilities of networking technologies, processing speed, algorithmic complexity due to the high number of active sensors, the massive volume of collected biomedical data, and the need for premium service quality in terms of reliability and delay. For example, a wireless electroencephalography (EEG) headset that measures the electrical activity of the brain with 29 channels, sampled at 512 Hz with two bytes per channel, generates approximately 107 MB of data per hour for one single patient, which requires to be processed, transmitted, stored and analyzed. Despite the promising features of 5G in terms of large spectrum bandwidth and fast transmission, the challenge remains in how to leverage such features efficiently in terms of cost and energy consumption. This motivates the use of the edge computing paradigm, which promotes smart ways to process medical data close to where they are collected (i.e., as close as possible to the edge of the network), in order to optimize the amount and quality of data communicated over 5G, hence, minimizing the delay, energy consumption, and cost associated with data delivery. A very important use case of using EEG measurements to monitor patients is epilepsy. In fact, characterized by recurrent seizures, epilepsy is a common brain disorder affecting around 1% of the global population. Potentially harmful consequences of epileptic seizures and the lack of a definite cure for a large number of patients encouraged alternative solutions that allow subjects to actively monitor their brain health through intelligent mobile sensing devices with seizure detection or prediction capabilities. EEG monitoring is the primary tool for the assessment of epileptic seizures and it involves analyzing the change in EEG activity before, during, and after seizure onsets. The purpose of seizure prediction is to alert the patient normally few minutes beforehand of a seizure occurrence in order to take precautionary measures. However, the problem of prediction based on EEG signals is highly challenging, especially in reducing the rate of false alarms. On the other hand, seizure detection tries to identify the onset of the seizure and possibly its offset. In this case, ultra-low delay is essential as a seizure can typically have a duration of few seconds and, thus, every fraction of a second matters. This constitutes an important and impactful, yet challenging, application scenario for 5G URLLC. In this project, we present challenges and develop solutions for designing effective sHealth systems for neurological applications using a holistic framework that captures end-user sensing, mobile device processing, radio access network connectivity, mobile edge computing, remote cloud computing and storage, combined with advanced signal analysis and machine learning intelligence. We further illustrate the presented framework via a detailed experimental use case on mobile epileptic seizure detection and predication as an example of a globally common neurological disease. In addition, we investigate efficient resource allocation over 5G/5G+ networks in order to transmit the measured health information in real-time, and to alert the user in case of an imminent seizure. We showcase our achievements via a testbed based on real measurement data, and implemented in collaboration with Hamad Medical Center (HMC) and Huawei in Qatar.
The percentage of chronic disease (CD) patients is climbing to reach almost one-fifth globally, posing immediate threats on healthcare expenditure (in Qatar it reaches ~2.5% of the national GDP), and rising causes of death (more than 76% of deaths in Qatar are owed to CDs). This calls for transforming healthcare systems away from one-on-one patient treatment, to improve services, access and scalability, while reducing costs. The deployment of mobile and wearable devices in healthcare along with the advances of wireless networking and cloud-based technologies will enable mobile health (mHealth) systems to operate in conjunction with invaluable sets of data that are amassed from wide range of sources. Smart Health (sHealth) can be considered the evolution of mHealth, where collected medical and physiological data can be efficiently mined at the patient level to better understand the patient context, hence optimizing the transmission and integration of diagnostic information from healthcare professionals at the cloud level, while facilitating immediate response in cases of emergency. Such concept is set to revolutionize healthcare delivery by giving CD patients better control of their medical situation and allow the public to continuously and smartly monitor their health conditions. Recent innovations are paving the way towards an even more interactive connectivity level with the ongoing developments towards the 5G cellular technology and the Tactile Internet, especially with the 5G massive machine type communications (mMTC) and ultra-reliable low latency communications (URLLC) use case scenarios. Combining extremely low latency with high availability and reliability, the Tactile Internet, based on 5G URLLC, will facilitate real-time, synchronous, haptic feedback with remote-control solutions. This will give rise to a great variety of opportunities for emerging technologies and services especially in the field of tele-health. With the prospective evolution towards next generation 5G networks, such services will benefit from faster connections, greater mobility, increased inter-device compatibility, and harmonization between different communications standards. Remarkably, in sHealth systems for neurological applications, continuous sensory data acquisition and rapid diagnostic feedback and medical intervention have the potential to positively impact the lives of a large portion of the global population who suffer from chronic brain illnesses and disorders. Yet, these impose strict constraints on data storage, capabilities of networking technologies, processing speed, algorithmic complexity due to the high number of active sensors, the massive volume of collected biomedical data, and the need for premium service quality in terms of reliability and delay. For example, a wireless electroencephalography (EEG) headset that measures the electrical activity of the brain with 29 channels, sampled at 512 Hz with two bytes per channel, generates approximately 107 MB of data per hour for one single patient, which requires to be processed, transmitted, stored and analyzed. Despite the promising features of 5G in terms of large spectrum bandwidth and fast transmission, the challenge remains in how to leverage such features efficiently in terms of cost and energy consumption. This motivates the use of the edge computing paradigm, which promotes smart ways to process medical data close to where they are collected (i.e., as close as possible to the edge of the network), in order to optimize the amount and quality of data communicated over 5G, hence, minimizing the delay, energy consumption, and cost associated with data delivery. A very important use case of using EEG measurements to monitor patients is epilepsy. In fact, characterized by recurrent seizures, epilepsy is a common brain disorder affecting around 1% of the global population. Potentially harmful consequences of epileptic seizures and the lack of a definite cure for a large number of patients encouraged alternative solutions that allow subjects to actively monitor their brain health through intelligent mobile sensing devices with seizure detection or prediction capabilities. EEG monitoring is the primary tool for the assessment of epileptic seizures and it involves analyzing the change in EEG activity before, during, and after seizure onsets. The purpose of seizure prediction is to alert the patient normally few minutes beforehand of a seizure occurrence in order to take precautionary measures. However, the problem of prediction based on EEG signals is highly challenging, especially in reducing the rate of false alarms. On the other hand, seizure detection tries to identify the onset of the seizure and possibly its offset. In this case, ultra-low delay is essential as a seizure can typically have a duration of few seconds and, thus, every fraction of a second matters. This constitutes an important and impactful, yet challenging, application scenario for 5G URLLC. In this project, we present challenges and develop solutions for designing effective sHealth systems for neurological applications using a holistic framework that captures end-user sensing, mobile device processing, radio access network connectivity, mobile edge computing, remote cloud computing and storage, combined with advanced signal analysis and machine learning intelligence. We further illustrate the presented framework via a detailed experimental use case on mobile epileptic seizure detection and predication as an example of a globally common neurological disease. In addition, we investigate efficient resource allocation over 5G/5G+ networks in order to transmit the measured health information in real-time, and to alert the user in case of an imminent seizure. We showcase our achievements via a testbed based on real measurement data, and implemented in collaboration with Hamad Medical Center (HMC) and Huawei in Qatar.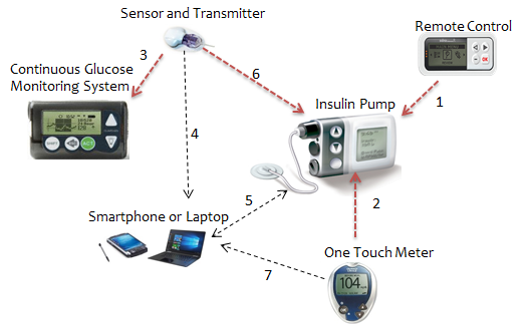 Wireless medical devices have been used to treat various diseases and to hold patients’ medical records. There are many different types of wireless medical devices, such as wireless insulin pumps, pacemakers, cardiac defibrillators, neuro stimulators, drug delivery systems, and so on. In the United States alone, 4.6 million pacemakers and implantable cardiac defibrillators (ICDs) were sold between 2006 and 2011. In 2007, there were approximately 375,000 pumps sold in the U.S., with this market expected to grow 9% annually between 2009 and 2016. Unfortunately, most of the existing wireless medical devices lack sufficient security mechanisms to protect patients from malicious attacks. With the rise in use of medical devices, security becomes a critical issue because attacks on wireless medical devices may harm or even kill patients. A number of attacks could be launched on these devices. Researchers from several groups (IBM, McAfee, UMass, Harvard, etc.) have demonstrated various attacks that can penetrate these devices. Actually, an insulin pump overdose injection has caused at least one death. Hence, it is critical to design effective security schemes to prevent attacks on the medical devices and therefore protect patients. Securing wireless medical devices is a challenging task due to their limited resources in terms of energy supply, processing power, storage space, and so on. For example, a medical device with a small ion-lithium battery storing about 3000 joules of energy is expected to operate for several years. A medical device manufactured in 2002 that is still being used today, contains as low as 8 KB storage. Due to the above reasons, traditional crypto-based security schemes cannot be applied to many of these medical devices. This project proposes fundamental research that is aimed to make medical devices secure and safe. We plan to develop light-weight and effective security schemes that will be portable and efficient when used in such small devices. The proposed project will advance the state-of-the-art of medical device security. The expected outcomes include (1) light-weight and effective security (safety) schemes that can detect malicious (accidental) overdoses from wireless infusion devices, (2) effective security schemes when patients are in emergency situations (e.g., coma), (3) near-field-communication-based security schemes for general wireless medical devices, and (4) other security schemes to defend various attacks on general wireless medical devices.
Wireless medical devices have been used to treat various diseases and to hold patients’ medical records. There are many different types of wireless medical devices, such as wireless insulin pumps, pacemakers, cardiac defibrillators, neuro stimulators, drug delivery systems, and so on. In the United States alone, 4.6 million pacemakers and implantable cardiac defibrillators (ICDs) were sold between 2006 and 2011. In 2007, there were approximately 375,000 pumps sold in the U.S., with this market expected to grow 9% annually between 2009 and 2016. Unfortunately, most of the existing wireless medical devices lack sufficient security mechanisms to protect patients from malicious attacks. With the rise in use of medical devices, security becomes a critical issue because attacks on wireless medical devices may harm or even kill patients. A number of attacks could be launched on these devices. Researchers from several groups (IBM, McAfee, UMass, Harvard, etc.) have demonstrated various attacks that can penetrate these devices. Actually, an insulin pump overdose injection has caused at least one death. Hence, it is critical to design effective security schemes to prevent attacks on the medical devices and therefore protect patients. Securing wireless medical devices is a challenging task due to their limited resources in terms of energy supply, processing power, storage space, and so on. For example, a medical device with a small ion-lithium battery storing about 3000 joules of energy is expected to operate for several years. A medical device manufactured in 2002 that is still being used today, contains as low as 8 KB storage. Due to the above reasons, traditional crypto-based security schemes cannot be applied to many of these medical devices. This project proposes fundamental research that is aimed to make medical devices secure and safe. We plan to develop light-weight and effective security schemes that will be portable and efficient when used in such small devices. The proposed project will advance the state-of-the-art of medical device security. The expected outcomes include (1) light-weight and effective security (safety) schemes that can detect malicious (accidental) overdoses from wireless infusion devices, (2) effective security schemes when patients are in emergency situations (e.g., coma), (3) near-field-communication-based security schemes for general wireless medical devices, and (4) other security schemes to defend various attacks on general wireless medical devices.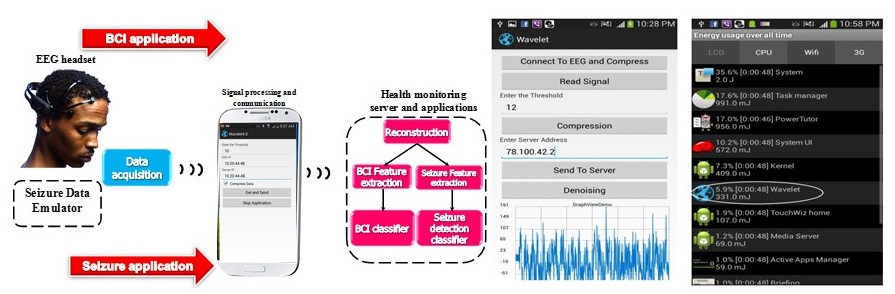
The underlying collaborative project aims at developing the first Qatar Healthcare Collaborative Network (QHCN), a novel generalized mHealth architecture for reliable, scalable, and effective patient monitoring and medical data management, leveraging sensors and smartphone technologies for connecting patient networks with medical infrastructure to facilitate remote patient treatment. In contrast to previous efforts in this domain, including our previous research, QHCN will adopt a holistic approach by focusing on the scalable signal processing of multiple heterogeneous modalities representing patients’ vital signals, and the effective communication amongst multiple patient networks, leveraging social networking paradigm for optimized data transport. The goal is the delivery of patients’ medical data (and/or features extracted from the data) to the mHealth infrastructure cloud, where the detection and classification of patient’s adverse events are carried.
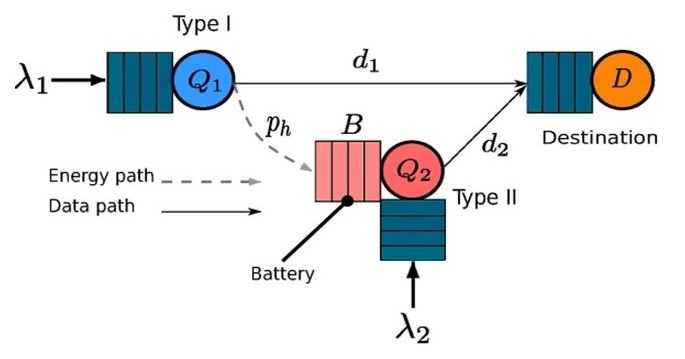
This project aims at designing a Green And Dense (GAD) wireless access network that leverage its multiple features (heterogeneity in coverage areas and data rates, cognitive radio capabilities, density) and translate the unquestionable complexity of the system into an opportunity for achieving optimality, or getting really close to it.
In order to face such a challenge, the GAD project takes the following actions:
- The first goal is to specify the network scenario and traffic requirements that at the time at which the project starts will be of utmost interest. In this phase of the project, the interaction with operators such as Vodafone Qatar or Telecom Italia will provide us with the right input. Along with the network scenario, we need to define metrics and models for energy consumption and traffic load estimation, due to the single network devices as well as to network-wide operations. Among the most important operations, we will consider spectrum sensing and we will identify the most performing mechanisms.
- Once the basic operations and network models are defined, the architecture of the wireless access networks is detailed, by specifying the functionalities implemented at the different entities as well as the way these entities interact and communicate with each other.
- Next, optimization and queuing-theoretic formulations will be used to derive a set of strategies aiming at determining
- As proof of concept and demonstration of the effectiveness and potentiality of the GAD system, both an in-lab small-scale testbed and an outdoor medium-scale demonstration will be developed to showcase the energy-efficient techniques and protocols proposed throughout the research work. The GAD testbed leverages multi-tier architecture to support heterogeneous wireless access network with dynamic spectrum access and on/off policies to realize energy-efficiency in dynamic and practical life scenarios.
In the first part of the project, the team has developed novel video encoding and network resource optimization mechanisms for fixed wireless battery-operated cameras deployed in strategic places onsite, hence provide the flexibility to move the cameras as the situation calls for it. The objective is to cover the site and address the limited energy capacity of the battery operated smart sensors, while providing real-time video delivery. This objective was achieved using the state-of-the-art in-network processing, which means, process the video information inside the network to minimize both the time spent in delivering the video and the energy consumed by all smart sensors. This will have the impact on maximizing the life-time of the sensors, hence reduce the human intervention (although not eliminate it) for maintaining such sensors through recharging.
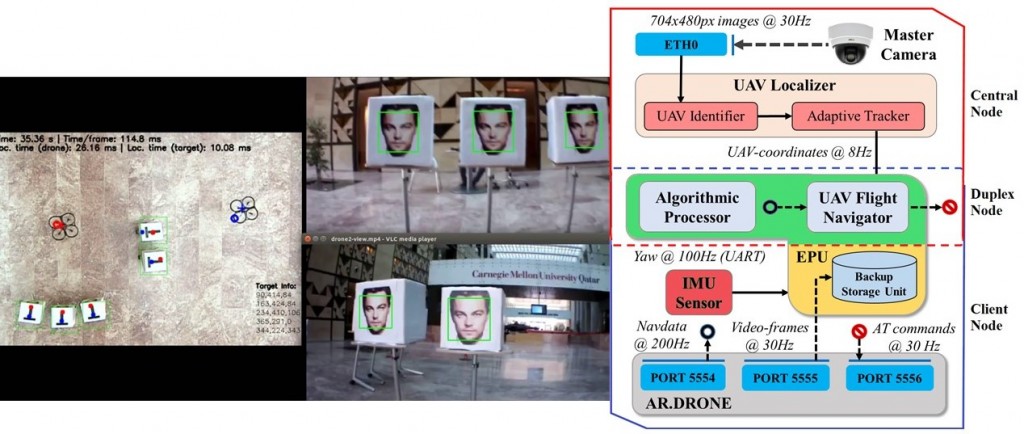
In the second part of the project, the team started to look into mobile cameras systems, particularly unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV), which can potentially eliminate the deployment of sensors onsite completely through leveraging mission-based flying sensing platforms, which can be used on-demand. The team has designed the first indoor multi-UAV platform, in which the UAVs can fly autonomously to cover the area and provide a monitoring and tracking platform, before they fly back to the base. The UAV-based system uses sophisticated localization, navigation, and networking mechanisms to control the UAVs, providing the ultimate flexibility for surveillance of static and dynamic environments.

The underlying collaborative project aims at developing novel spectrum sensing mechanisms, resource management strategies, and network protocols that are tailored for opportunistic real-time (ORT) communications. In contrast to previous efforts in this domain, ours will focus on delay-sensitive, connection-oriented opportunistic communications. Key CR functions, including spectrum sensing, dynamic channel assignment, and channel migration, as well as networking protocols (MAC, routing, etc.) will need to be tailored to this type of traffic. Our research agenda comprises the following three major thrusts:
- Active sensing strategies for ORT communications. We will consider practical sensing strategies, in which spectrum is sequentially sensed and probed. This so-called active sequential sensing aims at not only identifying spectrum holes, but also at probabilistically assessing the quality of the spectrum hole (i.e., allowable transmission rate) and its “durability” (i.e., how long the spectrum opportunity is expected to last for). In the presence of channel fluctuations and PU dynamics, a key question that will be addressed is when to stop sensing. We will address this problem in the context of optimal stopping theory. Our setup will account for the inherent uncertainty in channel sensing (captured through false alarm and misdetection probabilities), and will enable us to perform parametric optimization on the sensing and probing durations. A related, equally significant issue is that of channel migration in case of reemerging PU activity. In this case, the sensing process must be conducted under time constraints to ensure the continuity of the ongoing ORT session. Dynamic in-band and out-of-band sequential sensing and update of backup channels subject to timing constraints will be explored for this purpose.
- Efficient resource allocation strategies for multi-rate, multi-hop ORT flows. We will develop centralized and distributed power/rate allocation strategies that are tailored to ORT streams. To cope with the long-lived nature of these streams, we will conduct our optimizations at various time scales. We will also account for the rate demands of the transported flows (assuming a certain degree of elasticity) as well as potential channel migration during the lifetime of a flow.
- Novel distributed protocols for multi-hop ORT communications. We will design theory-inspired channel access and routing protocols for transporting ORT flows. In contrast to classic MAC protocols for CR networks, ours will target delay-sensitive, long-lived sessions. We will also address the notorious problem of link coordination in the absence of a priori established control channel. This problem is accentuated by the spatiotemporal variations in spectrum availability, which make it challenging for nodes to “rendezvous” and establish an initial dialogue between them. To address this problem, we will explore novel designs based on dynamic establishment of “control zones.” For routing protocols, we will consider novel metrics for path selection, geared more towards “spectral stability,” rather than throughput.
- Resource optimizations and protocols for ORT communications leveraging “cognitive relays”. We will explore the potential of cognitive relays as a means of facilitating ORT transmissions. Our purpose here is to combine the benefits of cooperative diversity and opportunistic communications, which opens the door for exciting yet challenging research issues. We will study the resource allocation problem in this context and analyze several fundamental tradeoffs. We will also develop corresponding channel access protocols that would enable such a concept in a distributed setting.
- Experimental evaluation. We will use a network testbed of USRP-v2 radios at Qatar University to experimentally demonstrate a sample of our optimized ORT protocols. This thrust is critical for advancing the technology maturity level of the proposed solutions from theory and simulations to implementation. It will also provide us with valuable insight into the subtle practical challenges of ORT communications.
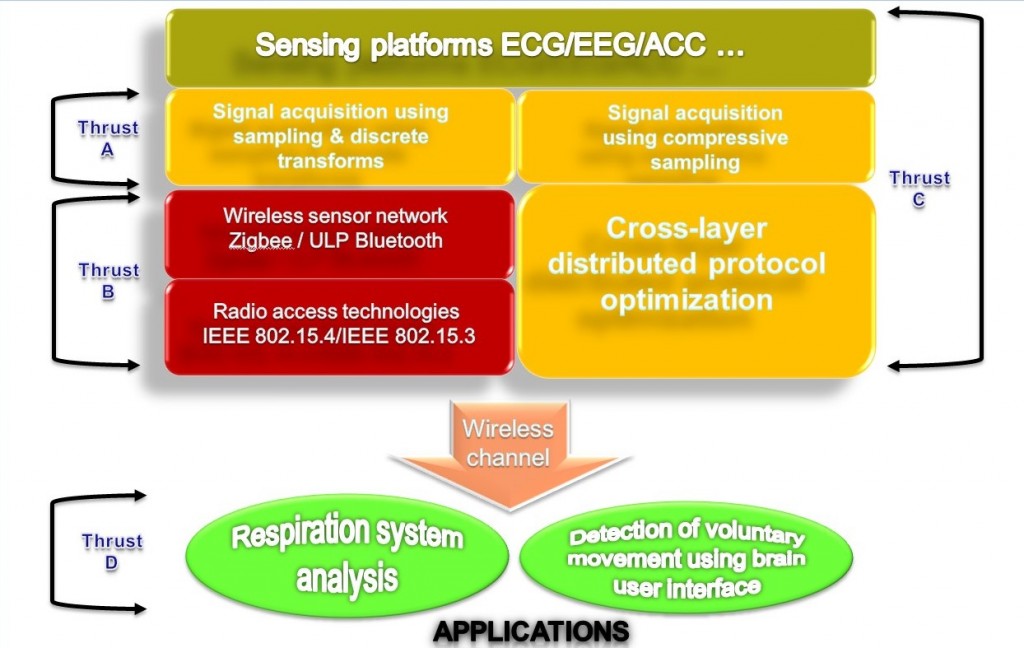
The overall goal of this project is to contribute to the development of the signal processing, protocol designs, cross-layer designs and sensor data processing techniques that will make WBASNs more efficient, reliable, and effective and thereby make their widespread deployment practical and commercially viable.
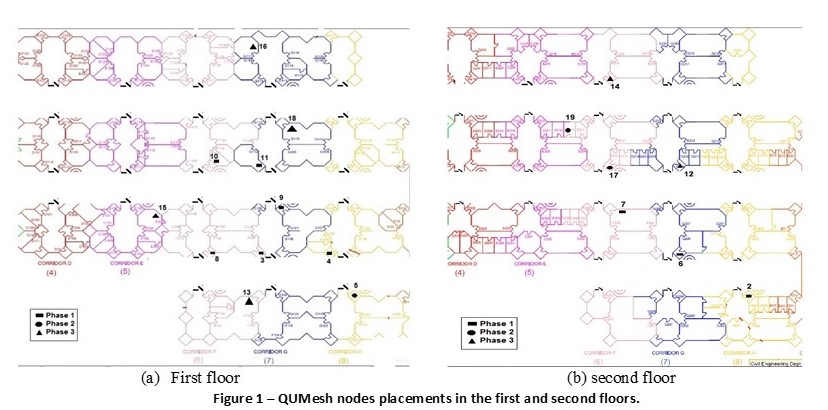
The joint Purdue-Qatar team proposes to develop a medium-scale mesh network testbed called QU-Mesh on the Qatar University campus, and investigate several fundamental research challenges in the wireless mesh networking technology. To achieve such long-term objective, the following specific aims will be sought:
- QU-Mesh Testbed Development and Deployment: We plan to develop and deploy a wireless mesh network testbed on the Qatar University campus, in the college of engineering. We will investigate how to pick deployment locations for individual mesh routers as well as the gateway(s) to balance the connectivity and maximize the coverage. We propose a 3-tier network architecture that optimizes the outdoor connectivity across the college cells, enhances the coverage within indoor building, and broadens the service provisioning for various types of end devices. We will also investigate various network management issues such as addressing, gateway translation, authentication, and security.
- High Performance Routing Protocol Design: We plan to develop a framework that systematically guides the design of high-throughput routing protocols for wireless networks that leverage recent development of “exotic” optimization techniques such as opportunistic routing and network coding. We will study how the framework can be used to guide the design of high-performance routing protocols that satisfy different application requirements. In particular, we will design, implement, and evaluate on the proposed testbed, several new protocols that exploit the rich design space exposed by the framework, and quantify the performance benefits of individual building-block techniques for each protocol.
- Resource Optimization for End-to-End Unicast/Multicast Multimedia Sessions: We plan to develop a cross layer framework for unicast and multicast end-to-end (E2E) sessions to maximize the network’s resource utilization while providing fairness amongst the E2E sessions. The proposed techniques will support heterogeneous multicast sessions and will guarantee steering the entire network towards optimal operating points in real-time, hence, react robustly to network changing conditions as they occur. Efficient optimization techniques will be sought to decompose the global problem into a group of sub-problems that can be solved in a modular structure. We plan to design and implement the distributed protocol that can realize the proposed techniques and preserve backward compatibility with existing network standards (i.e. 802.11j, WiMax, etc).
- Signal Propagation in Fading Channels, Interference Management: We will investigate how well the wireless signal propagates in the indoor/outdoor environment and what is its impact on the mesh network throughput. Fading channel models for indoor and outdoor environments will be studied. In the outdoor environment, the effect of different weather conditions such as high humidity and sandstorms, which are typical of the Qatari weather will be studied. For the indoor environment, the effect of unique cell structure of the engineering building in indoor channel modeling will be studied. We will utilize the network nodes themselves by extracting the RSSI information as well as use radiation measurements devices to build a statistical model for both the indoor and outdoor channels. The measurements taken can also serve as a guideline on interference issues from neighboring mesh nodes as well as from other sources such as cell phone bases stations and on campus WLAN. Techniques to mitigate as well as manage the effect of interference will be addressed.
