Research
Grants
2016-2019: NPRP9-224-1-049: Spatio-Temporal Composition of Sensor Cloud Services.
2010-2011: UREP 08- 029 – 1 – 007: Mining Write-Prints for Authorship Attribution in E-mail Forensics.
2010-2014: NPRP 09-778-2-299: Fault adaptive performance management.
2011-2015: NPRP 4 – 1165 – 2 – 453 : Advances in Biometrics via Narrowband Multispectral Imaging.
2012-2013: Qatar university Students Grant.
2013-2014: Qatar university Students Grant.
2014-2015: Qatar university Students Grant.
2015-2016: Qatar university Students Grant.
Some research and development projects
2006-2008: Projects with the Canadian National Defense.
Project 1: Coalition Warrior Interoperability Demonstration, 2008 (CWID’08) with Defense Research and Development, Canada–Valcartier (DRDC).
Role: Senior software solution architect and user interface analyst.
Tasks:
- Participated in designing CWID ’08 client-server software application for military command and control.
- Participated in designing and developing the software user interface of the client prototype.
- Participated in database, web-service development.
- Participated in the integration of various databases (Oracle, Sybase, etc.) and several remote web services to the application server and provisioned accessing them from CWID client application.
- Programmed using J2EE, JMS, JPF, XML, WSDL, Apache Geronimo, Oracle, Sybase, Eclipse, etc.
- Involved in high-quality document writing associated to the CWID’08 execution.
Project 2: Total Resource Visibility Project (TRV- Project) as a part of JCDS 21 standing offer contract with Defense Research and Development, Canada –Valcartier (DRDC).
Role: Senior software solution architect and user interface analyst.
Tasks:
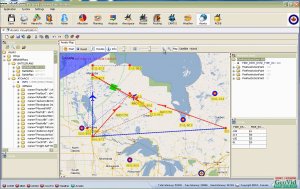
- Participated in Designing the software user interface of TRV-Prototype (see next picture)..
- Worked with DRDC-Professionals to understand the military requirements of assets visualization, data analysis and military logistic operations.
- Participated in rapid prototyping of TRV- Prototype to reflect planning of military logistic operations on a geographic information system.
- Participated in developing an advanced geographic information system (GIS) for the military assets visualization.
- Programmed using Java, XML technologies, Eclipse and Netbeans Editor, etc.
- Participated in Building all the user-interface using Java IDEs (Eclipse and Netbeans). Tasks:
- Role: User interface analyst, military command and control analyst, senior developer.
Project 3: Network Centric Distributed and Continual Planning Project (NCDCP- Project) with Defense Research and Development, Canada –Valcartier (DRDC).
- Contributed to the development of “Digital Cockpit” concept for military mission command and control in this project.
- Participated in designing and developing a middleware to support decision making in network-centric environment.
- Involved in designing and prototyping plug-in based software application where software modules can be added in run-time.
- Worked on several cutting-edge software technologies, including Java plug-in framework, web-service composition, XML technologies, geographic information systems, etc.
- Integrated various remote Java Web Services from a software application. Programmed using Apache Geronimo Server, Apache Tomcat Server, Oracle, Sybase, SOA, JMS, Java, JPF, XML, JavaScript, WSDL, BPEL, Eclipse, NetBeans, etc.
2007: A model checker for cryptographic protocols: The model checker uses a game theoretic approach to verify security flaws in cryptographic protocols.
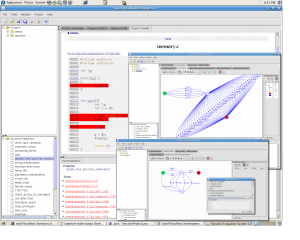
2007: A verification tool for finding security bugs in open source software: The tool uses a push down system model checker to check violation rules that can be expressed as temporal safety properties. A temporal safety property is expressed as a transition system that dictates the order of a sequence of operations (see next picture)..
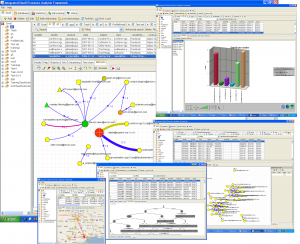
2007: An integrated Email forensics analysis framework: The framework implements advanced functionalities like statistic analysis, data mining, social networks, and geographic localization for a multi-staged analysis of an email corpus, to help forensic investigators collect clues and evidence (see next picture).
2003-2004: A tool for UML validation: The tool allows to verify a UML design against an OCL specification, and automatically generates Java code for both system and software quality assurance.
2002: A tool for telecommunication networks visualization and performance analysis: The tool called “Graph-Lab”, allows the graphical designing of a telecommunication network and its analysis.
1993-1997: An object oriented relational data base system: The system called “New Database Vision” (NDV) is in half way between a relational and an object oriented database system. NGV proposes an original approach for a rapid development of database applications with several interesting features, such as: semi graphics interfaces, all time customizable and self repair applications, with visual programming capabilities. The system handles more than 13 data types (int, float, radio button, checkboxes …), supports views, report generation and more. More than 10 applications have been developed using NDV and commercialized.
1999-2000: A self learning general purposes troubleshooter (expert system): The system, developed with CLIPS, can be taught by an expert in any field, and then used to solve problems in that field.
1989-1990: A Multimedia tutoring system: The system is an integrated environment, offering a graphics tool, a multi-text editor, a music editor and a Pascal-like programming language to develop electronic courses, tutorials and presentations.
1998-1999: An implementation of the fast Fourier transform using Transputers: The application is written in the language Occam, and can be set to run on different configurations of transputers.
1999-2000: A cross language internet search engine: The search engine uses a spider with a specific weighting technique to index the Internet, and a dictionary to retrieve results in several languages.
1994-2001: Others: Development of games and several scientific applications in deferent fields including: fuzzy logic, 3D Graphics, image and signal processing, probability and statistics, programming languages, artificial intelligence, operation research, graph theory, etc.
Abstracts of some contributions
- Hadjidj, R. and Boucheneb, H. (2011). Efficient reachability analysis for time Petri nets. IEEE Transaction on Computers, vol.60, no.8, pp.1085-1099
- Abstract: We proposed in this paper some efficient approaches, based on the state class graph method, to construct abstractions for the Time Petri Net (TPN) model, suitable to verify its linear or reachability properties. Experimental results have shown that these abstractions are very appropriate as both time and size are considerably reduced. For some tested models, abstractions that preserve reachability properties can be as many as 2,051 times smaller and more than 592 times faster to compute. For abstractions, which are over approximations (useful to prove that certain states are not reachable), gains can overpass 10,000 for both time and size
- Hadjidj, R. and Boucheneb, H. (2008). Improving state class constructions for CTL* model checking of time Petri nets. International Journal on Software Tools for Technology Transfer. STTT 10(2): 167-184.
- Abstract: The state space explosion is still one of the most challenging problems in formal verification using enumerative techniques. The challenge is even greater for real time systems whose state spaces are generally infinite due to time density. To use enumerative techniques with these systems, their state spaces need to be contracted into infinite structures that preserve properties of interest. We propose in this paper an efficient approach to construct a contraction of a real time system state space, which preserves its CTL* properties.
- Hadjidj, R. and Boucheneb, H. (2009). On the fly TCTL model checking for time Petri nets. Theoretical Computer Science. TCS 410(42): 4241-4261
- Abstract: In this paper, we show how to efficiently model check a subset of TCTL properties of a real time system, modeled as a time Petri net (TPN), using the state class method. The verification proceeds by augmenting the model of the real time system under analysis with a special model, called Alarm-clock, to allow the capture of relevant time events. A forward on-the-fly exploration is then applied on the resulting model’s state class space to verify a timed property. A relaxation operation on state classes is also introduced to further improve performances. Alarm-clock is the same for all properties, whereas the exploration technique is not. Three exploration techniques are presented to cover most interesting TCTL properties. We prove the decidability of our verification technique for bounded TPN models and compare it with the reachability algorithm implemented in the tool UPPAAL. Finally, we give some experimental results to show the efficiency of our verification technique.
PhD Thesis details
Title: Formal validation of real time systems
Thesis supervisor: Hanifa Boucheneb (Professor at the computer engineering department of l’Ecole Polytechnique of Montreal (University of Montreal)
Defense Date: Feb 2006
Abstract
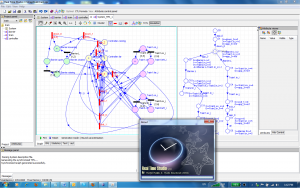
In this thesis, we are interested in real time systems, for which we propose some effective approaches to verify their timed and untimed properties. The retained verification technique is model-checking. Since the state space of a real time system is in general continuous and infinite, mainly due to the continuous nature of time, the application of model-checking requires an additional abstraction step to generate a discrete and finite abstract state space of the system. This state space must also preserve the properties of interest. From the point of view of untimed properties verification, our contributions are rather propositions to attenuate the state explosion problem. We start by defining a formal framework to characterize an abstract state model of a real time system vis-à-vis the properties it preserves, then we propose some abstract state models that preserve reachability, linear and branching properties. These properties can then be verified using classical model-checking methods. Furthermore, we show that our formal framework is more appropriate than the one proposed in the literature to characterize known abstractions of real time systems. For timed properties, we propose a temporal logic, and give its formal semantic, then we propose a forward on-the-fly verification technique, based on the so called state class method, and prove its decidability for all bounded Models. To evaluate our approach, we compare it to the reachability algorithm implemented in the tool Uppaal. In average, we can verify models 7 times faster than Uppaal, with lesser memory usage. For certain properties, the verification is more than 4000 times faster, with 110 times lesser memory usage. To validate our approaches we implemented them in our tool called Real-Time-Studio (see next picture).
Master Thesis Details
Title: Dynamic Graphs: A new paradigm for parallel and distributed computations
Supervisor: Professor Ainouche Ahmed (Professor at the university of Antilles and Guyane, France)
Defense Date: June 1994
Abstract
In this thesis, we propose a new paradigm for parallel and distributed computations we call “Dynamic Graphs”. A Dynamic Graph is in its structure similar to a graph of graph theory, with the possibility to associate dynamic sets of properties and behaviors to its arcs and vertices. A message queue is also associated with each arc and vertex of a dynamic graph for an asynchronous communication between its components. Through these possibilities, all components of a graph become active and can be set to participate together to solve problems in a parallel and distributed way by sending messages and messengers. A messenger is a message associated with a behavior. More than carrying simple information, a messenger can perform actions where ever it is sent, according to a well established set of rules. Typical actions of a messenger are: sending itself to specific destinations, inserting itself in the set of behaviors of the entity it has reached and change its properties, duplicate itself, destroy itself, etc. The paradigm is mainly inspired from biological activities in live organisms and can be seen as an actor model too. A tool called “New Graph Vision” (NGV), based on Dynamic Graphs, was designed and implemented in C++ under Windows. NGV has the structure of a graph editor, where the user can draw a graph and define, in a specific language, properties and behaviors for each vertex and link. The graph becomes dynamic and can be started for execution as if it was a distributed network of computers. The tool allowed us to propose some algorithms to solve problems related to networking and graph theory in an original way. Problems such as the coloring and the salesman problem, and systems such as Petri nets, neural networks, network protocols where treated successfully.
Research Interests
With the advance in technology, systems grow in complexity and become increasingly difficult to develop, verify and maintain. Real time systems are a category systems which behaviors take also into account timing constraints. These systems are in general concurrent, distributed and more difficult to construct and validate. In this context, formal methods are strongly recommended since they rely on sound mathematical bases. Formally verified systems enjoy a high degree of confidence, which allows their designers to be more persuasive when it comes to convince deciders for their installation.
My PhD research goal was to develop formal verification techniques to help construct more safe and reliable real time systems and telecommunication protocols. For this, several mathematical formalisms have been investigated and the Time Petri Net model (TPN model) was retained for its power to model both concurrency and timing constraints in a concise and natural way. However, the model has serious drawbacks when it comes to verification due to a lack of research in this field. The objective of my research was to overcome this limitation by proposing efficient approaches to verify timed and untimed properties of real time systems using model-checking techniques. Since the state space of a real time system is in general continuous and infinite, model-checking application requires an additional abstraction step to generate a discrete and finite abstract state space. This state space must also preserve properties we want to verify. For untimed properties, my contributions are propositions to attenuate the state explosion problem. I started first by defining a formal framework to characterize an abstract state model vis-à-vis the properties it preserves, then proposed some abstract state models for a real time system that preserve its reachability, linear and branching properties. These properties can then be verified using classical model-checking methods. For timed properties, I defined a temporal logic and proposed a forward on-the-fly verification technique, based on the so called state class method, then I proved its decidability for all bounded TPN Models. To evaluate the performance of my verification approach, I compared it with the model checking technique implemented in the tool UPPAAL which verifies timed automata modes. In average, I was able to verify TPN models more than ten times faster than UPPAAL for equivalent timed automata models, and with much lesser memory usage. For certain properties, the verification is more than 3400 times faster, with 110 times lesser memory.
Another outcome of my PhD work was Real Time Studio, a tool to model and verify real time systems. The tools allows for a modular design of real time systems using interpreted time Petri nets, and implements all my proposed approaches and several other functionalities related enumerative analysis of real time systems, including CTL, LTL, and TCTL model checkers, and a minimizer under bisimulation. The tool is under constant improvement and several extensions are expected, to widen the scope of its use. Two of these extensions are already in progress; one of them is related to the formal verification computer security, the other one deals with bioinformatics for the simulation of bio-pathways using Hybrid functional Petri Nets (see next picture).
Current Reserach
In the computer Security field, I am interested in developing new techniques and tools to verify security properties in open source software application using, mainly push down systems model-checking techniques. In computer forensics, I am interested in developing new techniques and tools to detect malicious activities in communication networks (including wireless networks), like Botnets detection and tracking, and authorship attribution in emails and instant messages. In Image processing I am interested in identifying new modalities for person identification based on multispectral image analysis.
In formal verification, I am interested in developing modular verification techniques for real time systems. These techniques attempt to overcome the state explosion problem inherent to model checking technique, by exploiting the modular structure naturally present in most system designs. Some approaches have already been proposed in the literature where partial order techniques are adapted to timed models. However the results are still not satisfactory to deal with industrial size modes. In parallel, I intend to explore how the verification techniques I proposed can be used to verify security properties for real time systems and cryptographic protocols, using timed extensions of Petri nets, process algebra and timed automata. The application of formal methods to hardware verification is another topic of real interest to me.
On another front, the application of formal methods in bioinformatics seems very promising. The simulation of bio-pathways using Hybrid functional Petri Nets has already proven very effective, and the implementation of such possibility in my tool Real time studio, would certainly open the door for reach collaborations with scientist in that field.
